
Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the G 1, S, and G 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. Meiosis II, in which the second round of meiotic division takes place in a way that is similar to mitosis, includes prophase II, prometaphase II, and so on. The genetic information is also mixed during this division to create unique recombinant chromosomes. Meiosis I reduces the number of chromosome sets from two to one. However, because there are two rounds of division, the stages are designated with a “I” or “II.” Thus, meiosis I is the first round of meiotic division and consists of prophase I, prometaphase I, and so on. Because the events that occur during each of the division stages are analogous to the events of mitosis, the same stage names are assigned. To achieve the reduction in chromosome number, meiosis consists of one round of chromosome duplication and two rounds of nuclear division. However, the starting nucleus is always diploid and the nuclei that result at the end of a meiotic cell division are haploid. Meiosis employs many of the same mechanisms as mitosis. In mitosis, both the parent and the daughter nuclei contain the same number of chromosome sets-diploid for most plants and animals. As you have learned, mitosis is part of a cell reproduction cycle that results in identical daughter nuclei that are also genetically identical to the original parent nucleus. The nuclear division that forms haploid cells, which is called meiosis, is related to mitosis. Gametes fuse with another haploid gamete to produce a diploid cell. In animals, haploid cells containing a single copy of each homologous chromosome are found only within gametes.
#DURING PROPHASE 1 OF MEIOSIS FULL#
Diploid organisms inherit one copy of each homologous chromosome from each parent all together, they are considered a full set of chromosomes.
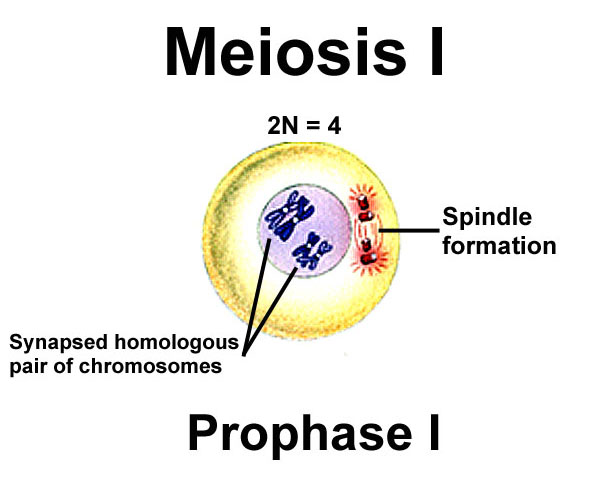
Homologous chromosomes are matched pairs containing genes for the same traits in identical locations along their length. Somatic cells are sometimes referred to as “body” cells. Most animals and plants are diploid, containing two sets of chromosomes in each somatic cell (the nonreproductive cells of a multicellular organism), the nucleus contains two copies of each chromosome that are referred to as homologous chromosomes. So, in addition to fertilization, sexual reproduction includes a nuclear division, known as meiosis, that reduces the number of chromosome sets. If the reproductive cycle is to continue, the diploid cell must somehow reduce its number of chromosome sets before fertilization can occur again, or there will be a continual doubling in the number of chromosome sets in every generation. Cells containing two sets of chromosomes are called diploid. Haploid cells contain one set of chromosomes. The number of sets of chromosomes in a cell is called its ploidy level.
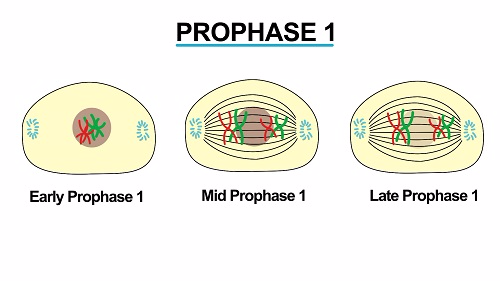
If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell contains two sets of chromosomes. Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. Explain the mechanisms within meiosis that generate genetic variation among the products of meiosis.Explain the differences between meiosis and mitosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
